pheatmap_advanced
Case 1
The datasets were provided by data-to-viz
library(tidyverse)
library(pheatmap)
library(ggplot2)
library(viridis)
library(kableExtra)
### dataset 1
data <- read.table("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/holtzy/data_to_viz/master/Example_dataset/13_AdjacencyDirectedWeighted.csv", header=TRUE)
# show data
data %>% head(3) %>% select(1:3) %>% kable() %>%
kable_styling(bootstrap_options = "striped", full_width = F)|
Africa |
East.Asia |
Europe |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Africa |
3.142471 |
0.000000 |
2.107883 |
|
East Asia |
0.000000 |
1.630997 |
0.601265 |
|
Europe |
0.000000 |
0.000000 |
2.401476 |
### the following function were embeded in pheatmap source code
scale_rows = function(x){
m = apply(x, 1, mean, na.rm = T)
s = apply(x, 1, sd, na.rm = T)
return((x - m) / s)
}
scale_mat = function(mat, scale){
if(!(scale %in% c("none", "row", "column"))){
stop("scale argument shoud take values: 'none', 'row' or 'column'")
}
mat = switch(scale, none = mat, row = scale_rows(mat), column = t(scale_rows(t(mat))))
return(mat)
}
generate_breaks = function(x, n, center = F){
if(center){
m = max(abs(c(min(x, na.rm = T), max(x, na.rm = T))))
res = seq(-m, m, length.out = n + 1)
}
else{
res = seq(min(x, na.rm = T), max(x, na.rm = T), length.out = n + 1)
}
return(res)
}
data.plot <- scale_mat(mat = data,scale = "column")
breaks <- generate_breaks(data.plot,n = 256,center = F)
pheatmap::pheatmap(mat = data.plot,
cluster_cols = F,
cluster_rows = F,
scale = "column",border_color = "white",
color = viridis(n = 256, alpha = 1,
begin = 0, end = 1, option = "viridis"),
breaks = breaks)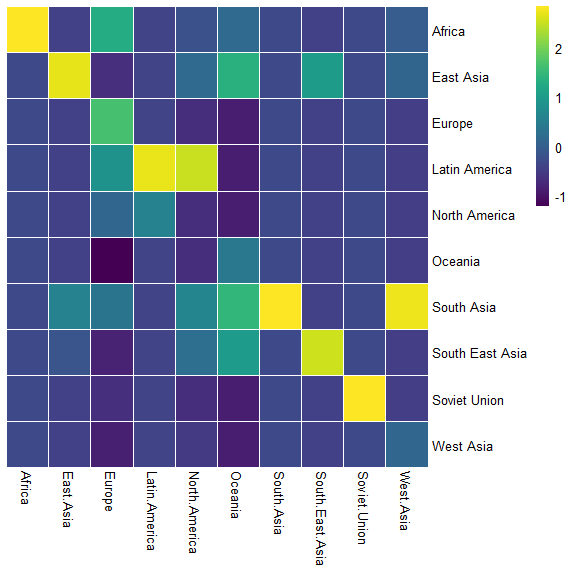
case 2
the codes were adapted from slowkow Sort dendrogram is very important
set.seed(42)
random_string <- function(n) {
substr(paste(sample(letters), collapse = ""), 1, n)
}
mat <- matrix(rgamma(1000, shape = 1) * 5, ncol = 50)
colnames(mat) <- paste(
rep(1:3, each = ncol(mat) / 3),
replicate(ncol(mat), random_string(5)),
sep = ""
)
rownames(mat) <- replicate(nrow(mat), random_string(3))
mat %>% as.data.frame %>% head(3) %>% select(1:3) %>% kable() %>%
kable_styling(bootstrap_options = "striped", full_width = F)|
1jrqxa |
1pskvw |
1ojvwz |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
abv |
9.6964789 |
9.172811 |
2.827695 |
|
nft |
0.9020955 |
15.575853 |
4.328376 |
|
xha |
2.6721643 |
3.127039 |
1.765077 |
split data into 3 groups, and increase the values in group1
making the heatmap
# install.packages("pheatmap", "RColorBrewer", "viridis")
library(pheatmap)
library(RColorBrewer)
library(viridis)
# Data frame with column annotations.
mat_col <- data.frame(group = col_groups)
rownames(mat_col) <- colnames(mat)
# List with colors for each annotation.
mat_colors <- list(group = brewer.pal(3, "Set1"))
names(mat_colors$group) <- unique(col_groups)
pheatmap(
mat = mat,
color = inferno(10),
border_color = NA,
show_colnames = FALSE,
show_rownames = FALSE,
annotation_col = mat_col,
annotation_colors = mat_colors,
drop_levels = TRUE,
fontsize = 14,
main = "Default Heatmap"
)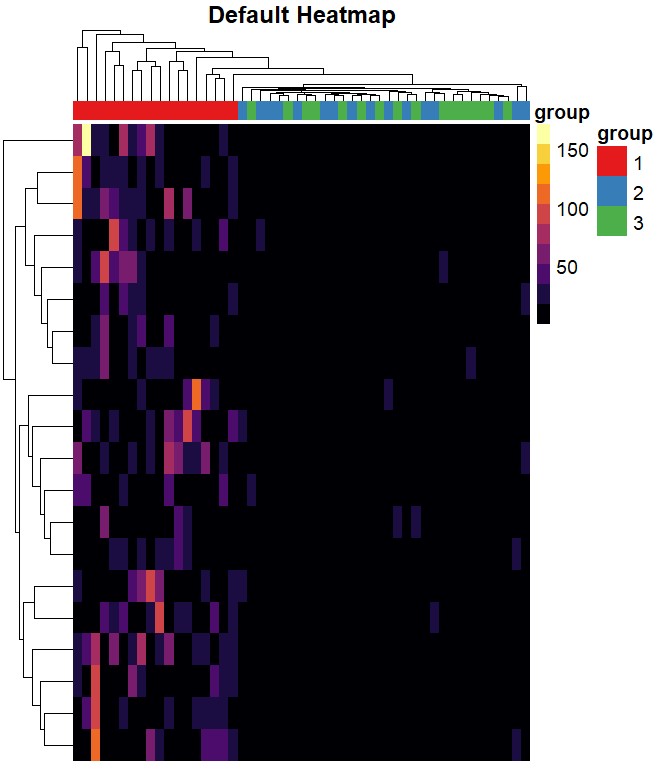
The default color breaks in pheatmap are uniformly distributed across the range of the data.
We can see that values in group 1 are larger than values in groups 2 and 3. However, we can’t distinguish different values within groups 2 and 3.
## ----uniform-color-breaks------------------------------------------------
mat_breaks <- seq(min(mat), max(mat), length.out = 10)
dat <- data.frame(values = as.numeric(mat))
## ----uniform-color-breaks-detail, fig.height=2, echo=FALSE---------------
dat_colors <- data.frame(
xmin = mat_breaks[1:(length(mat_breaks)-1)],
xmax = mat_breaks[2:length(mat_breaks)],
ymin = 0,
ymax = max(density(mat, bw = "SJ")$y),
fill = rev(inferno(length(mat_breaks) - 1)),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
ggplot() +
geom_rect(
data = dat_colors,
mapping = aes(
xmin = xmin, xmax = xmax, ymin = ymin, ymax = ymax, fill = fill
)
) +
geom_density(
data = dat,
mapping = aes(values),
bw = "SJ", color = "cyan"
) +
scale_fill_manual(values = dat_colors$fill) +
cowplot::theme_cowplot()+
theme(legend.position = "none") +
labs(title = "Uniform breaks")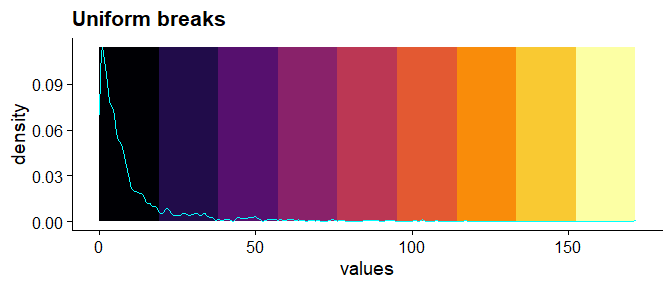
there are 6 data points greater than or equal to 100 are represented with 4 different colors.
dat2 <- as.data.frame(table(cut(
mat, mat_breaks
)))
dat2$fill <- inferno(nrow(dat2))
ggplot() +
geom_bar(
data = dat2,
mapping = aes(x = Var1, weight = Freq, fill = Var1),
color = "black", size = 0.1
) +
coord_flip() +
scale_fill_manual(values = dat2$fill) +
cowplot::theme_cowplot()+
theme(legend.position = "none") +
labs(y = "data points", x = "breaks",
title = "Number of data points per color")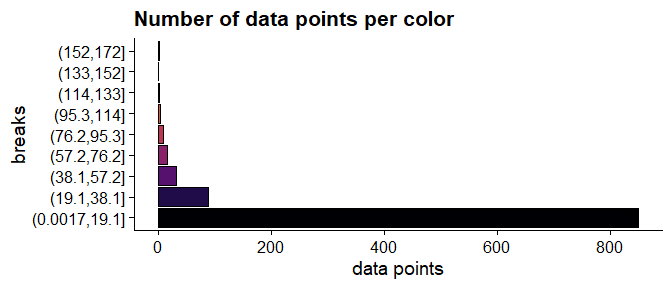
If we reposition the breaks at the quantiles of the data, then each color will represent an equal proportion of the data:
quantile_breaks <- function(xs, n = 10) {
breaks <- quantile(xs, probs = seq(0, 1, length.out = n))
breaks[!duplicated(breaks)]
}
mat_breaks <- quantile_breaks(mat, n = 11)lets see
dat_colors <- data.frame(
xmin = mat_breaks[1:(length(mat_breaks)-1)],
xmax = mat_breaks[2:length(mat_breaks)],
ymin = 0,
ymax = max(density(mat, bw = "SJ")$y),
fill = rev(inferno(length(mat_breaks) - 1)),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
ggplot() +
geom_rect(
data = dat_colors,
mapping = aes(
xmin = xmin, xmax = xmax, ymin = ymin, ymax = ymax, fill = fill
)
) +
geom_density(
data = dat,
mapping = aes(values),
bw = "SJ", color = "cyan"
) +
scale_fill_manual(values = dat_colors$fill) +
theme(legend.position = "none") +
labs(title = "Quantile breaks")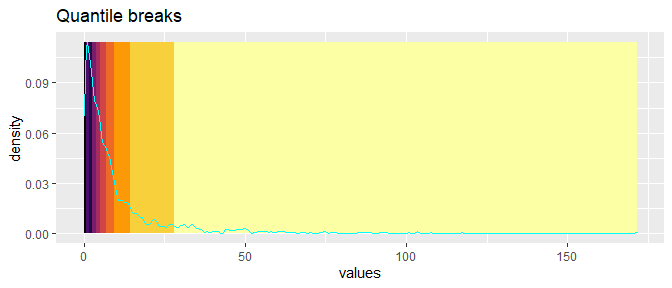
dat2 <- as.data.frame(table(cut(
mat, mat_breaks
)))
dat2$fill <- inferno(nrow(dat2))
ggplot() +
geom_bar(
data = dat2,
mapping = aes(x = Var1, weight = Freq, fill = Var1),
color = "black", size = 0.1
) +
coord_flip() +
scale_fill_manual(values = dat2$fill) +
theme(legend.position = "none") +
labs(y = "data points", x = "breaks",
title = "Number of data points per color")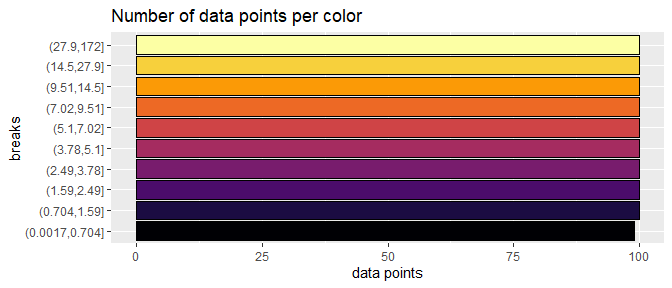
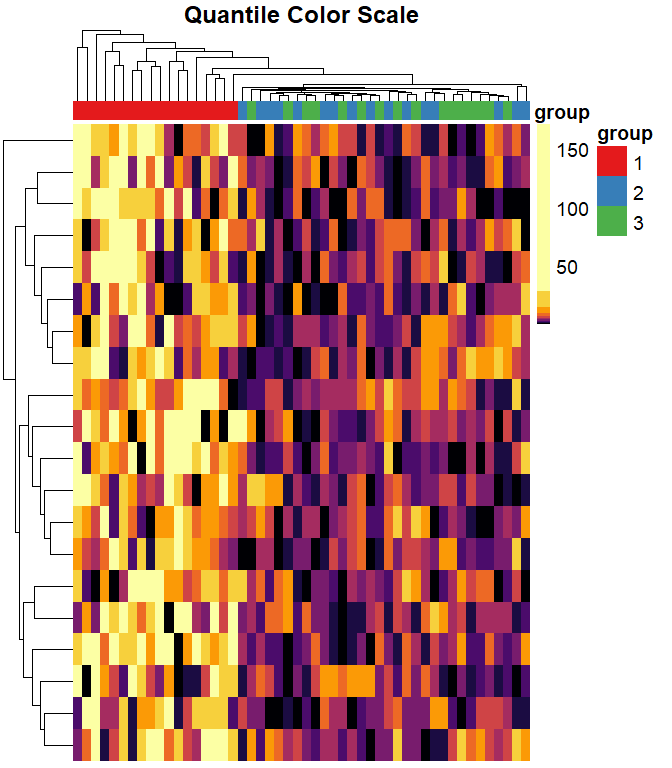
When we use quantile breaks in the heatmap, we can clearly see that group 1 values are much larger than values in groups 2 and 3, and we can also distinguish different values within groups 2 and 3:
pheatmap(
mat = mat,
color = inferno(length(mat_breaks) - 1),
breaks = mat_breaks,
border_color = NA,
show_colnames = FALSE,
show_rownames = FALSE,
annotation_col = mat_col,
annotation_colors = mat_colors,
drop_levels = TRUE,
fontsize = 14,
main = "Quantile Color Scale"
)
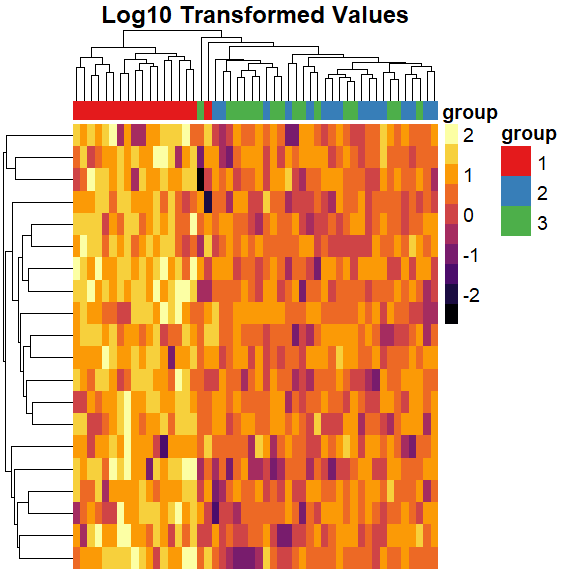
We can also transform data
pheatmap(
mat = log10(mat),
color = inferno(10),
border_color = NA,
show_colnames = FALSE,
show_rownames = FALSE,
annotation_col = mat_col,
annotation_colors = mat_colors,
drop_levels = TRUE,
fontsize = 14,
main = "Log10 Transformed Values"
)
sort dendrograms
library(dendsort)
mat_cluster_cols <- hclust(dist(t(mat)))
sort_hclust <- function(...) as.hclust(dendsort(as.dendrogram(...)))
mat_cluster_cols <- sort_hclust(mat_cluster_cols)
plot(mat_cluster_cols, main = "Sorted Dendrogram", xlab = "", sub = "")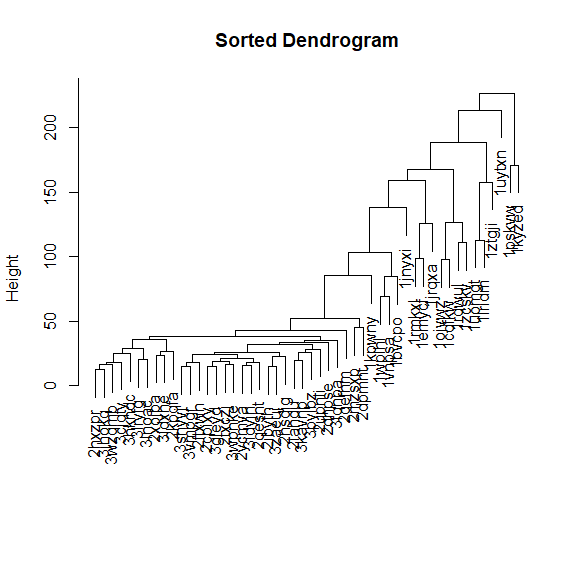
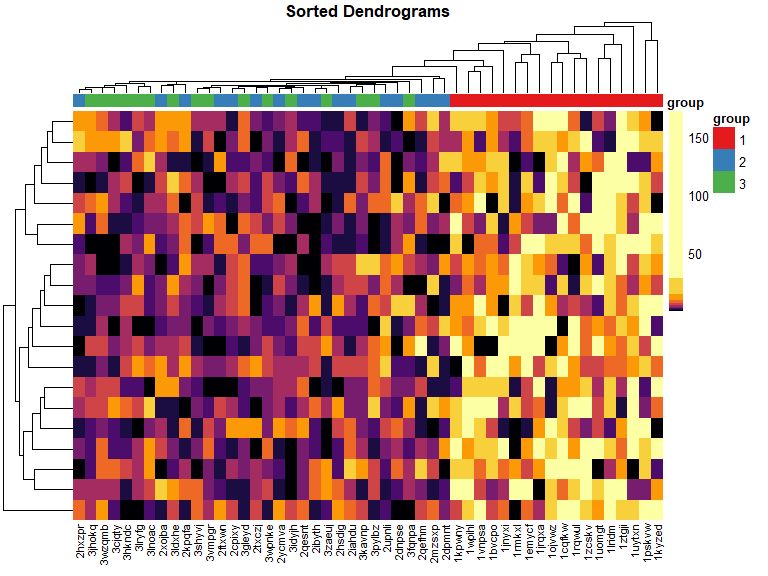
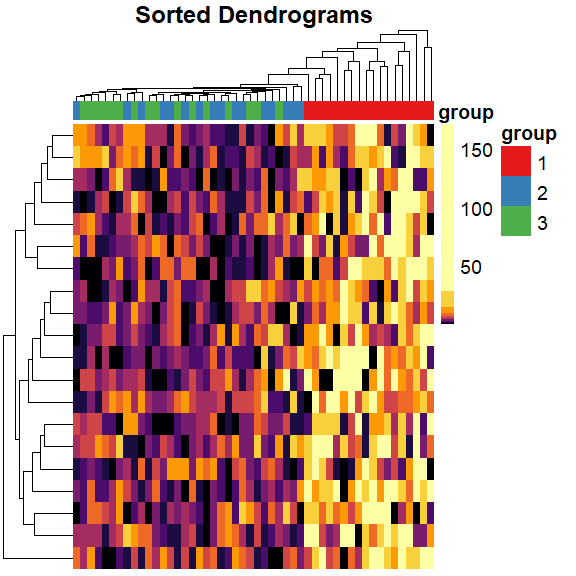
sort Dendrogram heatmap
mat_cluster_rows <- sort_hclust(hclust(dist(mat)))
pheatmap(
mat = mat,
color = inferno(length(mat_breaks) - 1),
breaks = mat_breaks,
border_color = NA,
cluster_cols = mat_cluster_cols,
cluster_rows = mat_cluster_rows,
show_colnames = FALSE,
show_rownames = FALSE,
annotation_col = mat_col,
annotation_colors = mat_colors,
drop_levels = TRUE,
fontsize = 14,
main = "Sorted Dendrograms"
)
change colnames angle
pheatmap(
mat = mat,
color = inferno(length(mat_breaks) - 1),
breaks = mat_breaks,
border_color = NA,
cluster_cols = mat_cluster_cols,
cluster_rows = mat_cluster_rows,
show_colnames = TRUE,
show_rownames = FALSE,
annotation_col = mat_col,
angle_col = 90,
fontsize_col = 8,
annotation_colors = mat_colors,
drop_levels = TRUE,
fontsize = 10,
main = "Sorted Dendrograms"
)